
In every flow system of fluid, there is a need to estimate the rate of flow. There are instances that the liquid has high heat capacity, and thus it needs a coolant flow meter. The idea is to let the fluid flow as you regulate the heat. The system uses a principle of thermal mass flow. The only addition is the principle of conservation of energy. These sensors are not affected by the properties of the flowing fluid. The pressure, temperature, do, and density of the fluid do not affect the flow rate measurement. These meters work differently from the volumetric meters. You do not need any calculations to get the flow rate. This factor has made the thermal mass flow meters gain popularity within a short time.
Coolant flow meters are highly applicable where there are engines and motors involved. They are used to monitor the engine and motor performance.
Thermal Mass Flow for Gases (Bypass Design)
When a thermal mass flow meter is mentioned, many people visualize a bypass sensor. It is one of the many thermal sensors in the fluid flow industry. With the bypass principle, some part of the fluid- mostly gasses- is diverted into a small capillary—the capillary acts as the sensor. There are two heating points (point A and point B). Both points are subjected to the same heat. Then the temperature of the fluid is taken at both ends. The difference is the flow rate of the fluid through the channel.
In the bypass principle, when the flow rate is low, the heat difference is high. The difference decreases as you increase the flow rate. The reason behind this is that a fluid at slow velocity will have enough time to heat up. But with speed, it has short contact time, thus insufficient time to heat up. These types of meters are applicable in channels with corrosive gases.
Heated Tube Design

The design has some similarities in the working principle as the bypass design. The difference is that there is no bypass channel for this kind of a meter. The heater and the sensor are attached to the external surface of the pipe. This design is used in liquids and gases. It is effective when using corrosive fluids. The sensor is placed far from the heater. This is because the temperature of the walls and the fluid is similar farther from the heater.
There are two operating modes in this system. In the first mode, you keep the power input constant and observe the rise in temperatures. In the other mode, you keep the difference in temperature contact. You then observe the amount of power needed to maintain the temperature. When you need a coolant flow meter, you use a cooling sensor on a pipe carrying hot fluids. The rest of the principles operate the same.
Air Velocity Probes
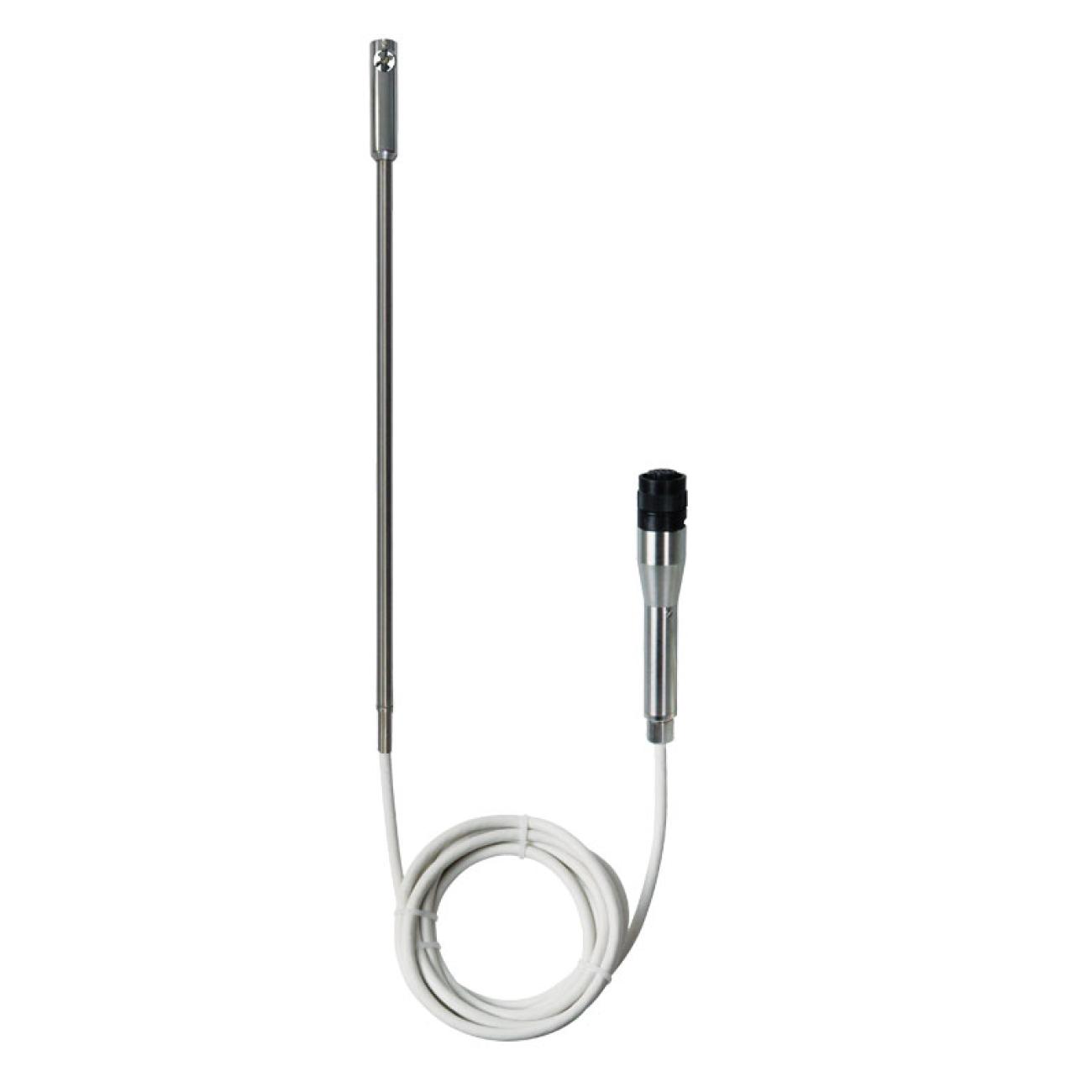

This design is a bit complex. Maybe that explains why they are not popular. They are mainly used to measure the flow rate of gasses. The system is not affected by dust particles within the gas. The first sensor should raise the heat of the fluid to 60 degrees Fahrenheit. It then maintains the heat that reaches the second sensor. As the flow rate increases, the power input at the first sensor should increase.
The design uses a principle of heat difference at two points. The heater and the sensor are inserted on the tube's interior, unlike the other two above.
Hot Wire Anemometer

This principle is applicable in the intrusive kind of thermal sensor. It is mainly used in gas mass flow measurement to reduce the coating of the sensor. The sensor wire is heated. As the gas passes past it, the wire cools down. The rate at which it cools down related to the flow rate.
Conclusion
The coolant flow meter is important in engines and motors. Thus, you should understand all the principles and fluid properties. It advises on the flow meter to select.




























