Preimplantation genetic diagnosis is used to test aneuploidy in the cases of low prognosis in patients opting for in vitro fertilization. It can also be instrumental in detection of hereditary single gene disorders, X linked diseases and recently, also for diagnosis of late onset diseases. Non-availability of embryos for transfer is likely to hinder demand for the preimplantation genetic diagnosis.
The world's first Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis was performed by Handyside, Kontogianni and Winston at the Hammersmith Hospital in London. Female embryos were selectively transferred in five couples prone to X-linked disease, leading to two twins and one singleton pregnancy.
In almost one third of couples opting for preimplantation genetic diagnosis cycles, the end result is that there is lack of normal transferrable embryos. This could be owing to the reason that sometimes women may show poor reaction to the given ovarian stimulation and as a result lesser eggs are produces. In other cases, despite there is an availability of a good level of embryos, their chromosomal value is located to be consistently abnormal.
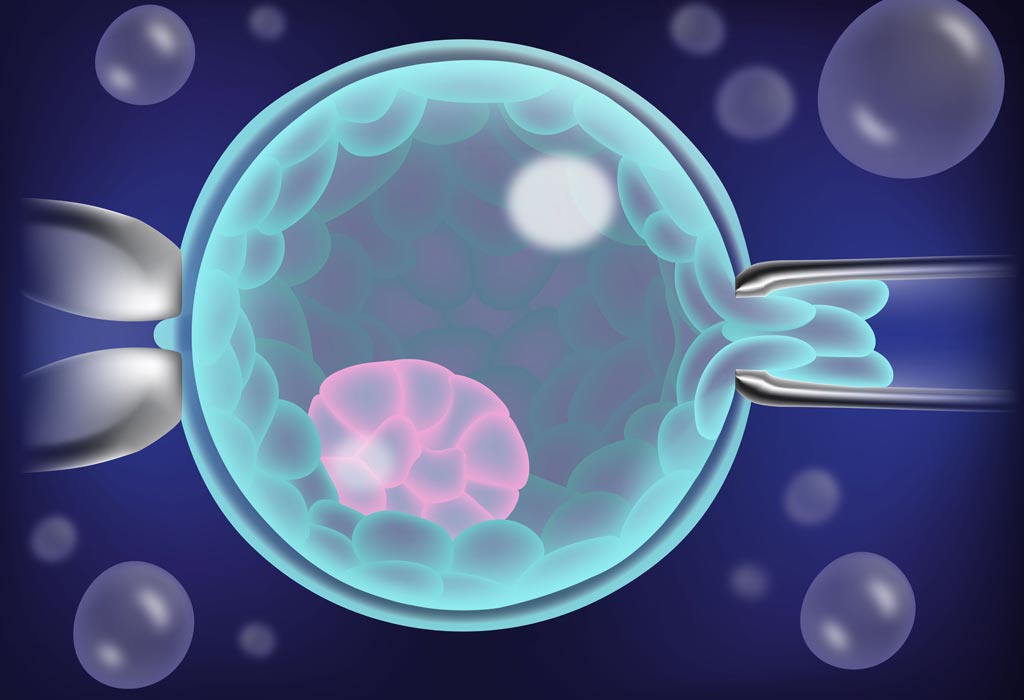
Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) is a lab procedure used in conjunction with in vitro fertilization (IVF) to lessen the chance of passing on inherited conditions.Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis (PGD or PIGD) is the genetic profiling of embryos ahead of implantation and sometimes even of oocytes ahead of fertilization. PGD is recognized as in an identical fashion to prenatal diagnosis. When used to screen for a certain genetic disease, its main advantage is so it avoids selective abortion, as the method makes it highly likely that the infant will soon be without any the disease under consideration.
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis involves testing the first embryo after in vitro fertilisation. A couple of cells (blastomeres) are removed at biopsy from the preimplantation embryo at the 6-10 cell stage (day 3 of development), thus allowing replacement to the uterus of unaffected embryos.
Finally, PGD is regarded as ethically sensitive because – like selective abortion after prenatal diagnosis – it amounts to a form of selective reproduction, in which only students are allowed to be born that are not afflicted with the disorders their parents were prone to transmitting.
Read More@ https://bit.ly/3up5Q1G




























